

 |
Gravimetría atómica Este proyecto utiliza una trampa magneto-óptica para estudiar la fuerza gravitacional. Desarrollamos técnicas para mejorar la interferometría atómica con el objetivo de medir fuerzas pequeñas, en particular del tipo gravitacional. Publicaciones -G. Ramírez-Meléndez, A. López-Vázquez, H.G. Ochoa, L. Jiménez, R.J. Hernandez y E. Gomez, “Optical frequency filtering for Raman beams,” Rev. Sci. Instrum. 95, 103203 (2024). -J. M. Cervantes y E. Gomez, “Effect of an aperture in atomic gravimetry,” JOSA A 41, 881 (2024). -E. Zuniga, E. Gomez y L.O. Castanos-Cervantes, “Precision limits of magnetic T3-atomic gravimetry due to atomic cloud expansion,” Phys. Rev. A 109, 013304 (2024). -A. López-Vázquez, R.J. Hernández y E. Gomez, “Tunable locking of calcite narrow frequency filters through modulation switching,” Rev. Sci. Instrum. 94, 083001 (2023). -J. De la Rosa, E. Gomez y V.M. Valenzuela, “Star shape interferometer with reduced vibration sensitivity,” Rev. Mex. Fis. 69, 031302 (2023). -A. López-Vázquez, M.A. Maldonado, E. Gomez, N.V. Corzo, E. De Carlos -López, J.A. Franco Villafañe, K. Jiménez-García, J. Jiménez-Mier, J.L. López-González, C.J. López-Monjaraz, J.M. López-Romero, A. Medina Herrera, R. Méndez-Fragoso, C.A. Ortiz, H. Peña, J. Raboño Borbolla, F. Ramírez-Martínez y V.M. Valenzuela, “Compact laser modulation system for a transportable atomic gravimeter,” Opt. Express 31, 3504 (2023). -M.A. Maldonado, W.M. Pimenta, J.A. Franco Villafañe y E. Gomez, “Elimination of spatial Rabi frequency modulation by sideband suppression with a calcite crystal,” Appl. Phys. B 127, 170 (2021). -J.M. Cervantes, M.A. Maldonado, J.A. Franco-Villafañe, T. Roach, V.M. Valenzuela y E. Gomez, “Selection of a Raman beam waist in atomic gravimetry,” OSA Contin. 4, 1996 (2021). -G.A. Olivares-Rentería, D.A. Lancheros-Naranjo, E. Gomez and J.A. Franco-Villafañe, "Quantum gravimetry in the same internal state using composite light Raman pulses," Phys. Rev. A 101, 043613 (2020). -A. López Vázquez, Y.M. Torres, M.S. Billión, W.M. Pimenta, J.A. Franco-Villafañe and E. Gomez, “Experimental generation of a flat-top beam profile in a stable ring cavity,” Opt. Lett. 44, 4428 (2019). -N. Arias, L.J. González, V. Abediyeh and E. Gomez, “Frequency locking of multiple lasers to an optical cavity,” J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 35 (10), 2394 (2018). -N. Arias, V. Abediyeh, S. Hamzeloui y E. Gomez, "Low phase noise beams for Raman transitions with a phase modulator and a highly birefringent crystal," Opt. Exp. 25 (5), 5290 (2017). -S. Hamzeloui, D. Martínez, V. Abediyeh, N. Arias, E. Gomez and V. M. Valenzuela, "Dual atomic interferometer with a tunable point of minimum magnetic sensitivity," Phys. Rev. A 94, 033634 (2016). -S. Hamzeloui, N. Arias, V. Abediyeh, D. Martínez, M. Gutiérrez, E. Uruñuela, E. del Rio, E. Cerda-Méndez, E. Gomez, "Towards Precision Measurements at UASLP," J. Phys. 698, 012011 (2016). -T. Matos y E. Gomez, "Space-Time Curvature Signatures in Bose-Einstein Condensates," Eur. Phys. J. D. 69, 125 (2015). -L.O. Castaños, E. Gomez, "Model for a phase-space selector using microwave transitions," Phys. Rev. A 89, 013406 (2014). -V.M. Valenzuela, S. Hamzeloui, M. Gutiérrez, E. Gomez, “Multiple isotope magneto-optical trap from a single diode laser,” J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 30, 1205 (2013). -V.M. Valenzuela, L. Hernández, E. Gomez, “High power rapidly tunable system for laser cooling,” Rev. Sci. Instrum. 83, 015111 (2012). -S. Martínez, L. Hernández, D. Reyes, E. Gomez, M. Ivory, C. Davison, S. Aubin, “Fast, small and low vibration mechanical laser shutters,” Rev. Sci. Instrum. 82, 046102 (2011). |
| |
 |
Gravimetría con MOEMS Este proyecto utiliza sensores de masa resorte para la determinación precisa de la aceleración gravitacional, aprovechando la tecnología MEMS combinado con mediciones ópticas. Publicaciones -Alejandro Sandoval, Roberto Hinojosa, Daniel Teran, Josue Hernandez, Eduardo Gomez, Victor M. Valenzuela, Francisco Cesar Delgado, Juan Ponce-Hernandez, Jesus J. Alcantar-Peña, Randall Guevara-Betancourt y Joselin Almaguer, “Electronics for a DC readout of a MEMS gravimeter with very high amplification and small drift,” Rev. Sci. Instrum. 96, 125003 (2025). -Randall Guevara-Betancourt, Luis Rodríguez-Sosa, Joselin Almaguer, Alfredo Aguillón-Robles, Vsevolod Yutsis, Damiano Sarocchi, Luis A. Rodríguez-Sedano, Oscar Guevara-Mansilla, Eduardo Gomez, Alejandro Sandoval y Margarito Tristán-González, “Interaction of tectonic systems in the origin of monogenetic volcanism of the Ventura Volcanic Complex, Mexico,” J. South Am. Earth Sci. 169 105849 (2025). -V.M. Valenzuela, D. Teran, A. Sandoval, E. Gomez, J.A. Franco-Villafañe, J.J. Alcantar-Peña y J. Ponce-Hernandez, “Three robust temperature-drift compensation strategies for a MEMS gravimeter,” J. Appl. Phys. 133, 234501 (2023). |
| |
 |
Detección molecular Raman coherente En éste proyecto buscamos un método efectivo para detereminar si dos moléculas interaccionan para formar un compuesto. La detección la implementamos mediante un interferómetro que mide las variaciones de fase relativa en un par de haces Raman. Publicaciones -J.M. Cervantes Martínez, E. Gomez, W.M. Pimenta y J.H. Marines Cabello, “A hybrid microwave-optical interferometer for off-resonance two-photon detection,” J. Phys. B 58, 205001 (2025). |
| |
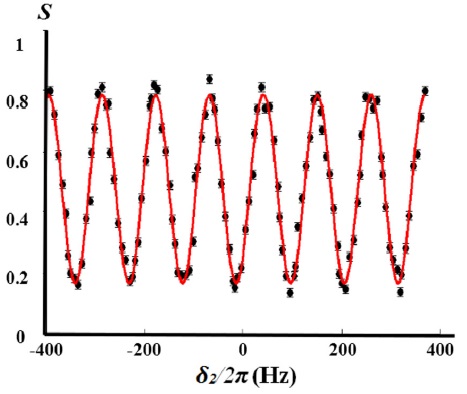
 |
Espectroscopia de francio para el estudio de la fuerza débil Este proyecto es parte de la colaboración FrPNC en TRIUMF en Vancouver, Canadá, dirigida por Luis Orozco (Joint Quantum Institute) y Gerald Gwinner (Universidad de Manitoba). Francio es el más pesado de los metales alcalinos y por lo tanto tiene un núcleo grande y a la vez una estructura atómica relativamente simple. El núcleo grande amplifica los efectos de la fuerza débil y utilizamos las técnicas sensibles de la espectroscopia atómica para medir sus débiles efectos. Nosotros estamos interesados en particular en estudiar las corrientes neutrales débiles entre nucleones dentro del núcleo. El efecto principal de dicha interacción es introducir un momento que viola la paridad llamado el momento anapolar. Nosotros medimos dicha violación detectando una transición hiperfina que solo está permitida debido al momento anapolar. Estas mediciones incrementarán nuestra comprensión sobre la fuerza débil dentro del núcleo. Este proyecto evolucionó a partir del trabajo en francio hecho por el grupo de Luis Orozco, donde logramos capturar grandes cantidades de francio en una trampa magneto-óptica y estudiamos su estructura atómica. Aquí pueden leer el comunicado de prensa sobre nuestra reciente corrida experimental. Para informacion general del proyecto ver: -E. Gomez, S. Aubin, G. D. Sprouse, L. A. Orozco, D. P. DeMille, “Measurement method for the nuclear anapole moment of laser-trapped alkali-metal atoms,” Phys. Rev. A 75, 033418 (2007) -E. Gomez, L. A. Orozco, G. D. Sprouse, “Spectroscopy with trapped francium; advances and perspectives for weak interaction studies,” Rep. Prog. Phys. 69, 79 (2006). Otros miembros de la colaboración: Prof. G. Gwinner (University of Manitoba), Prof. L.A. Orozco (Joint Quantum Institute), Prof. G.D. Sprouse (Stony Brook University), Dr. J.A. Behr (TRIUMF), Dr. K.P. Jackson (TRIUMF), Dr. M.R. Pearson (TRIUMF), Prof. V.V. Flambaum (University of New South Wales), Prof. S.A.M. Aubin (College of William and Mary) Publicaciones adicionales: -M. R. Kalita, J. A. Behr, A. Gorelov, M. R. Pearson, A. C. DeHart, G. Gwinner, M. J. Kossin, L. A. Orozco, S. Aubin, E. Gomez, M. S. Safronova, V. A. Dzuba and V. V. Flambaum, “Isotope shifts in the 7s - 8s transition of francium: Measurements and comparison to ab initio theory,” Phys. Rev. A 97, 042507 (2018). -R. Collister, J. Zhang, M. Tandecki, S. Aubin, E. Gomez, G. Gwinner, L.A. Orozco, M.R. Pearson and J.A. Behr, “Photoionization of the francium 7P3/2 state,” Can. J. Phys. 95, 234 (2017). -J. Zhang, R. Collister, K. Shiells, M. Tandecki, S. Aubin, J. A. Behr, E. Gomez, A. Gorelov, G. Gwinner, L. A. Orozco, M. R. Pearson y Y. Zhao, "Efficient inter-trap transfer of cold francium atoms," Hyp. Inter. 237, 150 (2016). -J. Zhang, M. Tandecki, R. Collister, S. Aubin, J. A. Behr, E. Gomez, G. Gwinner, L. A. Orozco, M. R. Pearson y G. D. Sprouse, "Hyperfine Anomalies in Fr: Boundaries of the Spherical Single Particle Model," Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 042501 (2015). -M. Tandecki, J. Zhang, S. Aubin, J.A. Behr, R. Collister, E. Gomez, G. Gwinner, H. Heggen, J. Lassen, L.A. Orozco, M.R. Pearson, S. Reader y A. Teigelhöfer, "Offline trapping of 221Fr in a magneto-optical trap from implantation of an 225Ac ion beam," J. Instr. doi:10.1088/1748-0221/9/10/P10013 (2014). -R. Collister, G. Gwinner, M. Tandecki, J.A. Behr, M.R. Pearson, J. Zhang, L. Orozco, S. Aubin y E. Gomez, "Isotope shifts in francium isotopes 206-213Fr and 221Fr," Phys. Rev. A 90, 052502 (2014). -M. Tandecki, J. Zhang, R. Collister, S. Aubin, J.A. Behr, E. Gomez, G. Gwinner, L.A. Orozco y M.R. Pearson, “Commissioning of the Francium Trapping Facility at TRIUMF,” J. Inst. doi:10.1088/1748-0221/8/12/P12006 (2013). -S. Aubin, J.A. Behr, G. Chen, R. Collister, V.V. Flambaum, E. Gomez, G. Gwinner, K.P. Jackson, D. Melconian, L.A. Orozco, M.R. Pearson, M.C. Ruiz, D. Sheng, Y.H. Shin, G.D. Sprouse, M. Tandecki, J. Zhang y Y. Zhao, “The Francium Facility At TRIUMF,” AIP Conf. Proc. 1525, 530 (2013). -S. Aubin, J.A. Behr, R. Collister, V.V. Flambaum, E. Gomez, G. Gwinner, K.P. Jackson, D. Melconian, L.A. Orozco, M.R. Pearson, D. Sheng, G.D. Sprouse, M. Tandecki, J. Zhang and Y. Zhao, "Atomic parity non-conservation: the francium anapole project of the FrPNC collaboration at TRIUMF," Hyp. Inter. 214, 163 (2013). -S. Aubin, E. Gomez, J.A. Behr, M.R. Pearson, D. Sheng, J. Zhang, R. Collister, D. Melconian, V.V. Flambaum, G.D. Sprouse, L.A. Orozco and G. Gwinner, "The FrPNC Experiment at TRIUMF: Atomic Parity Non-Conservation in Francium," AIP Conf. Proc. 1441, 555 (2012). -S. Aubin, E. Gomez, J.A. Behr, M.R. Pearson, D. Sheng, J. Zhang, R. Collister, D. Melconian, Y. Zhao, V.V. Flambaum, G.D. Sprouse, L.A. Orozco and G. Gwinner, "Atomic parity non-conservation in francium: The FrPNC experiment at TRIUMF," Il Nuovo Cimento 35(4), 85 PAVI (2011). -E. Gomez, S. Aubin, R. Collister, J.A. Behr, G. Gwinner, L.A. Orozco, M.R. Pearson, M. Tandecki, D. Sheng and J. Zhang, "The FrPNC Experiment, weak interaction studies in Francium at TRIUMF," J. Phys. 387, 012004 (2012). -D. Sheng, L.A. Orozco, E. Gomez, “Preliminary studies for anapole moment measurements in rubidium and francium,” J. Phys. B 43, 074004 (2010). -E. Gomez, S. Aubin, L.A. Orozco, G.D. Sprouse, E. Iskrenova-Tchoukova, M.S. Safronova, “Nuclear magnetic moment of 210Fr: A combined theoretical and experimental approach,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 172502 (2008). -A.P. Galvan, Y. Zhao, L.A. Orozco, E. Gomez, A.D. Lange, F. Baumer, G.D. Sprouse, “Comparison of hyperfine anomalies in the 5S1/2 and 6S1/2 levels of 85Rb and 87Rb,” Phys. Lett. B 655, 114 (2007). -G. Gwinner, E. Gomez, L.A. Orozco, A.P. Galvan, D. Sheng, Y. Zhao, G.D. Sprouse, J.A. Behr, K.P. Jackson M.R. Pearson, S. Aubin, V.V. Flambaum, “Fundamental symmetries studies with cold trapped francium atoms at ISAC,” Hyperfine Interactions 172, 45 (2006). -E. Gomez, F. Baumer, A. D. Lange, G. D. Sprouse , “Lifetime Measurement of the 6s Level of Rb,” Phys. Rev. A 72, 012502 (2005). -E. Gomez, L. A. Orozco, A. Perez Galvan, and G. D. Sprouse, “Lifetime Measurement of the 8s Level in Francium,” Phys. Rev. A 71, 062504 (2005). -E. Gomez, S. Aubin, L. A. Orozco, and G. D. Sprouse, “Lifetime and hyperfine splitting measurements on the 7s and 6p levels in rubidium,” J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 21, 2058 (2004). -S. Aubin, E. Gomez, L. A. Orozco, and G. D. Sprouse, “Lifetimes of the 9s and 8p levels of atomic francium,” Phys. Rev. A 70, 042504 (2004). -S. Aubin, E. Gomez, K. Gulyuz, L. A. Orozco, J. Sell, G. D. Sprouse, “Francium developments at Stony Brook,” Nucl. Phys. A 746, 459C (2004). -S. Aubin, E. Gomez, L. A. Orozco, and G. D. Sprouse, "Lifetime measurement of the 9s level of atomic francium," Opt. Lett. 28, 2055 (2003). -S. Aubin, E. Gomez, L. A. Orozco, and G. D. Sprouse, "High efficiency magneto-optical trap for unstable isotopes," Rev. Sci. Instr. 74, 4342 (2003). -G. D. Sprouse, S. Aubin, E. Gomez, J. M. Grossman, L. A. Orozco, M. R. Pearson, and M. True, "Atomic probes of electromagnetic and weak interactions with trapped radioactive atoms, " Eur. Phys. J. A. 13, 239 (2002). -S. Aubin, E. Gomez, J. M. Grossman, L. A. Orozco, M. R. Pearson, G. D. Sprouse, and D. P. Demille, "Francium spectroscopy and a possible measurement of the nuclear anapole moment," Proceedings of the XV International Conference on Laser Spectroscopy, Edited by S. Chu, V. Vuletic, A. J. Kemand and C. Chin, World Scientific, Singapore (2002) p. 305. |
| |
FRET de moléculas individuales El proyecto utiliza la técnica de FRET (Forster Resonance Energy Transfer) a nivel de moléculas individuales. La excitación de un fluoroforo se transfiere a un segundo fluoroforo cercano. La eficiencia de transferencia depende de la distancia, y por lo tanto el método es útil para medir distancias pequeñas. La medición de la excitación para moléculas individuales requiere de detección muy sensitiva a nivel de fotones individuales. Aplicaremos esta técnia para estudiar sistemas biológicos. El proyecto es en colaboración con Prof. Jaime Ruiz (IF UASLP), y el Prof. Alfredo Mendez (IF UASLP) Hemos demostrado que las terminales de la molécula de RNA permanecen a una distancia pequeña (y casi constante) independientemente de la longitud del RNA -N. Gerling, J.A. Mendez, E. Gomez y J. Ruiz-Garcia, “The separation between mRNA-ends is more variable than expected,” FEBS Open Bio doi:10.1002/2211-5463.13877 (2024). -P.L. Hernández-Adame, U. Meza, A.A. Rodríguez-Menchaca, S. Sánchez-Armass, J. Ruiz-García y E. Gomez, “Determination of the size of lipid rafts studied through single-molecule FRET simulations,” Biophys. J. 120, 2287 (2021). -A. Bañuelos-Frías, V.M. Castañeda-Montiel, E.R. Alvizo-Paez, E.A. Vazquez-Martinez, E. Gomez, J. Ruíz-García, “Thermodynamic and mechanical properties of DMPC/Cholesterol mixed monolayers at physiological conditions,” Front. Phys. 9, 636149 (2021). - N. Leija-Martínez, S. Casas-Flores, R.D. Cadena-Nava, J.A. Roca, J.A. Mendez-Cabañas, E. Gomez y J. Ruiz-Garcia, "The separation between the 5'-3' ands in long RNA molecules is short and nearly constant," Nucleic Acid Research 42, 13963 (2014). |
| |
|